
2
Dense Air Industry Insight 2024
INDUSTRY INSIGHT
STREAMLINING INDOOR
CONNECTIVITY
Written by:
Stephanie Atkinson,
Compass Intelligence

3
Dense Air Industry Insight 2024
This paper was written by Stephanie Atkinson on behalf of Dense
Air Networks to provide an independent overview into the changing
face of the telecoms industry as new deployment, ownership and
service models take hold.
While the ideas and principles outlined incorporate extensive research and con-
versations with experts, this paper serves only as a moment in time outlook.
For more information on this report contact Stephanie
at Compass Intelligence directly:
www.compassintelligence.com
Acknowledgement

4
Dense Air Industry Insight 2024
Introduction
Carriers are Not Funding In-Building Cellular
Modernization
Cellular Connectivity Should Simply be SEAMLESS
Solutions Review
Working with the Right Partner
1.0
2.0
3.0
4.0
5.0
6.0
Our Growing Reliance on In-Building Cellular
4.01 Signal Penetration Issues
4.02 Equipment Proximity
4.03 Accelerated Data Usage
4.04 Massive Trafc
4.05 Legacy & Latency
4.07 Secure Connectivity
4.06 Expertise & Skillset Gaps
4.08 Single Carrier
5.01 Wi-Fi
5.02 Distributed Antennae System (DAS)
5.03 Small Cell and Neutral Host Small Cell (NHSC)
Index
2.01 Example Use Case: Hospitality
2.02 Example Use Case: Commercial Real Estate
2.03 Example Use Case: Multi Dwelling
Indoor cellular connectivity challenges
cellShare™
7.0

5
Dense Air Industry Insight 2024
5
1.0 Introduction
In today’s hyper-connected world, robust cellular connectivity
within buildings is not just an amenity it’s a fundamental pillar of
modern infrastructure, vital for enhancing productivity, safety, and
tenant and guest satisfaction.
Cellular connectivity is increasingly becoming a must-have for venue owners,
property managers, tenants and guests, reecting our modern reliance upon
a seamless voice and data experience. Properties spanning ofces, hospitals,
hotels, multi-family residences and retail stores now must ensure quality wireless
across their premises to remain competitive.
In nearly every industry, cellular is used for connecting assets and operations,
people and devices. We increasingly require a working cellular connection all
the time, wherever we are. The requisite cellular experience is seamless outdoors
and indoors, regardless of the building, the elevation (top of a high rise or deep
underground in a parking garage), or population density. Poor user experiences
such as dropped calls or failed data sessions result in increased user frustration,
and in some cases, lost revenue for venues spanning hotels, hospitals, commercial
real estate and retail stores.
6
Dense Air Industry Insight 2024
While cellular carriers such as AT&T, T-Mobile and Verizon are focused on
building outdoor 5G networks, indoor cellular connectivity solutions have
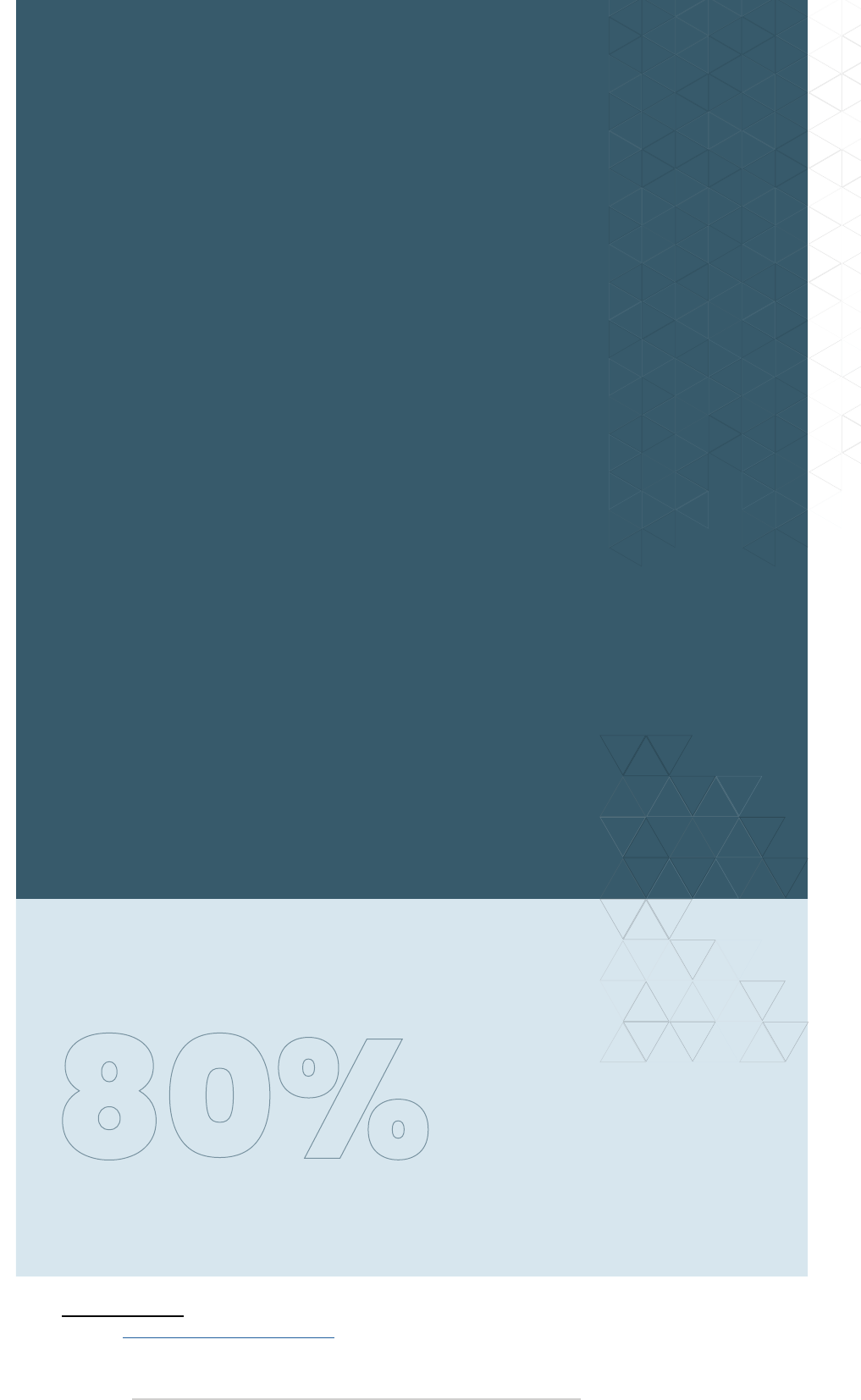
not kept up with the growing demand; this is particularly important as 80%
of cellular data is generated indoors.
1
Deploying carrier networks within buildings has historically posed
difculties, as cellular signals must navigate through frequency deecting
walls to reach a high concentration of users and devices. Structures that
commonly present challenges for indoor connectivity include multi-story
ofce or residential buildings, underground facilities like parking garages,
and venues featuring thick concrete walls or multi-layered glass.
While the telecom industry has been faced with indoor connectivity issues
for several decades, the problem is dramatically worsening. Modern
sustainable building materials, such as low-E glass with metallic coatings,
deect signals preventing the higher frequencies used in 5G to penetrate
effectively indoors. As 5G rolls out and we use more sustainable building
materials while consuming more data, indoor connectivity will suffer.
With businesses increasingly depending on cellular solutions and the
demand for specialized services like private networks growing, key
questions emerge: What solutions and partners are available to wireless
carriers and venue owners to help them enhance coverage, increase
capacity, and nance networks?
This paper explores the barriers to achieving ubiquitous multi-carrier
inbuilding connectivity and examines the various solutions, including
traditional approaches such as Distributed Antenna Systems (DAS) and
Wi-Fi, as well as disruptive neutral host small cell (NHSC) technologies. This
paper will analyze how the features and benets of these solutions vary in
providing a seamless cellular experience and the various implementation
partners available to a building owner.
1 Ericsson Mobility Report (2024)
80% of all cellular
data is generated indoors.
1

7
Dense Air Industry Insight 2024
In commercial real estate, cellular connectivity is
essential to support a variety of business operations
and employee needs. Employees depend on mobile
devices for seamless communication, collaboration,
and access to cloud-based services, regardless of their
specic location within a large ofce building.
Strong cellular signals ensure that calls and data
services are reliable, which is crucial for business
communications, especially for visitors or employees
who may not have immediate access to the ofce
Wi-Fi. Furthermore, robust cellular connectivity is
indispensable for emergency communications and
for enabling modern IoT-based ofce systems, such
as smart thermostats and security devices. Property
owners, managers, and developers recognize the crucial
role of cellular coverage in enhancing the lease value of
properties.
In hospitality, hotels need to deliver a secure, connected
work experience for business travelers while enabling
vacationers to surf the web and make calls back home.
Large events and conferences can massively increase
cellular trafc, compounding the problem for discrete
periods of time. A hotel therefore needs a network that
can handle high peak capacity and many different
users moving in and out of the premises.
2.0 Our Growing Reliance on
In-Building Cellular
Lack of coverage indoors is a growing issue for venue owners and
enterprises, and demands improvement, particularly as the roll
out of 5G threatens to aggravate the issue. During the pandemic,
individuals grew accustomed to the mobility of cellular networks as
they adapted to more exible work routines. Today, workers expect
to maintain work calls from home, during commutes, in parking
areas, or while riding an elevator.
Commercial
Real Estate
Hospitality

8
Dense Air Industry Insight 2024
In residential settings, especially multi-oor or
multi-dwelling units (MDUs) managed by property
management companies, there has traditionally been
a focus on xed-line connectivity. However, the rise in
remote work has made all-day cellular connectivity
a necessity for many tenants while smart home
technologies such as smart locks, thermostats, and
security cameras require a wireless connection. Quality
cellular connectivity can signicantly enhance resident
satisfaction and make a property more attractive to
potential renters or buyers.
In retail, particularly in large stores, cellular connectivity
has become crucial. Consumers use it to check
online offers while shopping in-store and to access
retail-specic applications, and store managers and
IT(Information Technology) staff use it to manage front-
of-house displays and demonstrations. As consumers
increasingly rely upon their cellphones to support their
shopping, retail stores without quality connectivity may
lose customers and sales.
Cellular connectivity is vitally important in healthcare
to ensure seamless communication throughout the
facility. In the fast-paced environment of a hospital,
doctors, nurses, and other healthcare professionals rely
heavily on mobile devices to communicate quickly and
efciently about patient care, access medical records,
and receive real-time updates. Strong cellular signals
are crucial for maintaining connectivity, especially in
buildings with complex layouts and dense materials
that might obstruct signals. Additionally, patients and
visitors benet from reliable cellular service to stay in
touch with loved ones and manage personal affairs
during hospital stays. This connectivity is not just about
convenience; it’s a critical component of modern
healthcare operations and patient safety, facilitating
better outcomes and enhancing the overall hospital
experience.
Residential
Retail
Healthcare

9
Dense Air Industry Insight 2024
In parking garages, cellular connectivity is crucial for
safety, convenience, and operational efciency. These
structures, which are often underground and enclosed,
can interfere with mobile signal reception, making it
difcult for users to make calls or use data services.
Enhanced cellular connectivity ensures that drivers and
pedestrians can contact emergency services if needed,
receive mobile payments, and use navigation apps
seamlessly. For parking management, strong signals
support the integration of smart parking solutions, such
as real-time space availability updates and automated
access controls, improving the overall user experience
and optimizing garage operations.
Across various industries, there are notable
similarities and differences in needs and
challenges. Primary stakeholders of structures,
buildings, and venues must identify the right
solutions for several crucial reasons:
Mobile connectivity is vital for operations such as
transactions, communications, and data access.
Inadequate cellular service can result in lost productivity
and revenue and potentially harm the reputation of the
facilities.
Seamless cellular connectivity serves as a competitive
advantage, helping to attract customers and
differentiate establishments from their competitors.
Dependence on cellular operators for connectivity
solutions can lead to delays and limited control,
potentially causing stakeholders to lag in adopting
modern technologies.
Proactive investment in infrastructure and technology
can future-proof businesses, keeping them abreast
of evolving customer expectations and technological
advancements.
Parking Garages
Cellular connectivity serves as the foundation for
innovation and digital transformation across industries.
To provide further context for the growing demand of
indoor cellular, let’s examine use case examples in
hospitality, commercial real estate, and multi-dwelling
buildings.

10
Dense Air Industry Insight 2024
The hospitality industry primarily aims to deliver exceptional guest experiences
to enhance revenue retention, increase occupancy, and foster repeat business
or loyalty. Establishments like hotels, casinos, and resorts face the challenge of
providing consistent connectivity both inside and outside their premises.
Venues often host various events like conferences, business meetings, weddings,
concerts, and sporting events. Particularly in urban areas, large venues can
experience network congestion due to the high volume of attendees using their
mobile devices. The goal for venue owners and managers is to ensure a high-
quality experience for attendees from the moment they arrive until they leave.
Wireless connectivity is crucial in enhancing this experience, facilitating various
guest interactions including services, food ordering, payments, entertainment,
mobile app usage, and access to key amenities. Increasingly, guest services
are migrating to smartphones, with many venues offering mobile apps that
streamline the guest experience by integrating multiple services.
Consider a scenario where you attend an event in downtown:
Driving through the city, you depend on a reliable cellular connection for navigation
and to direct you to the proper parking garage. Once parked, you might use a
phone app to pay for parking. As you walk to the venue, you might need to locate
your friends, access your digital ticket or reservation, make purchases, and nd
your seating or room — all relying on robust wireless services both outside and
inside the venue. If security is a concern, you might opt to avoid public Wi-Fi and
use your smartphone for all these activities.
2.01 Example Use Case: Hospitality

11
Dense Air Industry Insight 2024
Other crucial guest experiences reliant on mobile
communications include:
Charging electric vehicles (EV)
Taking calls or working in a restaurant, bar, or café
Arranging rideshares or food deliveries
Navigating from your hotel to a destination
Equally important is the employee experience, which
directly impacts guest services. Employees place
added demands on cellular networks to ensure they
can provide seamless and high-quality service.
Key areas where wireless connectivity enhances the
venue experience include:
Parking garage management
Point of Sale (POS) systems for kiosks or merchandising
carts
Access control or patron screening
Security camera systems
Mobile transactions by on-site staff
Management of on-site equipment and venue assets
2.02 Example Use Case: Commercial Real Estate
The commercial real estate industry has faced substantial challenges in recent
years, especially during the pandemic, which led to lease losses and non-
renewals, causing declines in occupancy rates and lease prices and affecting
the sector’s nancial performance.
Currently, the U.S. Class A ofce market is undergoing a transition known as
“ight to quality,” where tenants are migrating to newer ofces with amenities
and equipped with innovative technology and strong security systems.
To bounce back from the pandemic’s impacts and effectively adapt to the
present economic conditions, real estate stakeholders need to focus on
providing high-quality experiences for tenants and customers. Essential to this
is seamless connectivity, which allows employees to choose between wired and
wireless connections for their daily operations. Ensuring comprehensive wireless
and cellular access within and around ofce buildings is crucial.
Employees depend on uninterrupted connectivity for a range of activities,
including calls, chats, training, collaboration, and meetings. According to the
NAIOP, the Commercial Real Estate Development Association, connectivity is
the second most important criterion for ofce space tenants, preceded only by
location (NAIOP Summer 2021).

12
Dense Air Industry Insight 2024
Real estate owners and managers are thus compelled to offer
modern and secure facilities with attractive ofce amenities
to draw and keep tenants. In a competitive market, such
amenities are crucial differentiators that signicantly affect
tenant satisfaction and retention.
The following ofce activities rely on cellular communications:
Occupant communications
EV charging stations in parking lots
Security and surveillance (cameras, access control, facial
recognition)
Parking garage access
Conference and AV rooms
Common areas (lunch and break areas)
Building systems and management (BMS, HVAC, lighting,
energy)
Connected building assets (digital signage, occupancy
sensors, hot desking solutions)
Connectivity is the second most
important criterion for ofce space
tenants, right after location.
1
1 NAIOP, (Summer 2021)

13
Dense Air Industry Insight 2024
During the pandemic, multi-dwelling units (MDUs) became critical
spaces as many tenants worked from home and adhered to
quarantine measures.
This shift resulted in increased demands on building infrastructure and services,
as tenants used these systems extensively for both work and leisure. Like hotels,
MDUs and residential facilities often include adjacent or underground parking
garages for employees and residents. There is also mounting pressure to ensure
seamless cellular connectivity both indoors and outdoors. Effective cellular
coverage and services are often highlighted as amenities to attract residents
and inuence lease agreements.
2.03 Example Use Case: Multi Dwelling
The following activities rely heavily on wireless:
Security and surveillance (cameras, access control, facial
recognition)
Kiosks and front desk services
Amenity access or services
Building systems and management (BMS, HVAC, lighting,
energy)
Connected building assets (voice activated assistants, smart
smart security systems and applicances)
Occupant communications
EV charging stations in parking spots

15
Dense Air Industry Insight 2024
3.0 Carriers are Not Funding
In-Building Cellular Modernization
As cellular use and networks evolve, questions arise as to who will nance the
incremental infrastructure needed to modernize.
Carriers are conducting cost-benet analyses to decide whether to pursue
infrastructure projects, balancing the potential for less-than-ideal customer
experiences against economic realities. For in-building extension projects,
carriers typically prioritize large marquee venues, such as stadiums, airports,
and convention centers, and forsake investing in sub-1MM sq. ft buildings such
as ofces, hospitals, hotels, retail stores, and multi-family residences.
Even if a carrier does choose to invest in a property, it is likely only to build the
network for its own use case, rather than one that can support its competitors.
Building owners should be wary of working with just one carrier if they want a
system to support all service providers.
The owners of these smaller properties have traditionally hesitated to invest in
cellular infrastructure improvements themselves, deterred by a lack of technical
expertise and concerns about costs, while expecting network operators to
shoulder the nancial burden.
Furthermore, many stakeholders may not recognize the full scope
of connectivity challenges or their detrimental effects on customer
experiences and business operations. Thankfully, there are affordable and
exible solutions available. Building owners and property managers, as
key stakeholders, are well-positioned to lead efforts to enhance network
connectivity, improving the experience for all involved.
Before discussing these solutions, it is important to understand the
challenges in greater depth.

16
Dense Air Industry Insight 2024
No cellular coverage= frustrated customers & employees
Proximity to the radio access network (RAN) is critical
Data usage is expected to double over the next 6 years
High trafc and densly populated areas strain the nework
Signal Penetration Issues
Equipment Proximity
Accelerated Data Usage
Massive Trafc
Latency & Legacy
Expertise & Skillset Gaps
Secure Connectivity
Single Carrier
Delays & lags in data transmission due to aging hardware
IT teams lack the time or skillset to manage new cellular solutions
Robust security is essential for data protection and privacy
The challenges facing the industry to provide a seamless experience
are complex. Let’s explore these eight variables that signicantly
impact the success or failure of indoor cellular experiences.
4.0 Cellular Connectivity
Should be SEAMLESS
A network that supports multiple networks is paramount

17
Dense Air Industry Insight 2024
4.01 Signal Penetration Issues
As we transition from LTE to 5G, signal penetration
becomes more challenging. 5G signals, with
their higher frequency and shorter wavelength
compared to 4G/LTE, struggle to penetrate
physical structures like building walls. A weak
outdoor signal follows users indoors, leading to an
unsatisfactory indoor experience that fails to meet
consumer and operational requirements. This
presents signicant challenges, as poor cellular
connectivity hinders business operations. It’s
simple: no cell service or weak cell service means
employees become less effective, less productive,
and more frustrated.
Employees need reliable phone access for both
business and personal purposes. The quality of
calls or video streaming can signicantly affect
the perception end-users have of the network
and the building or company. Additionally, many
enterprise assets are monitored, tracked, and
managed using cellular communications, both
public and private.
4.02 Equipment Proximity
As we expand our mobile footprint and increase
remote working, the distance between radio
equipment, signals, and end-users becomes a
critical factor in ensuring seamless connectivity.
The core infrastructure, transport, and radio
access network (RAN) are vital for delivering
5G services. Proximity to the RAN or cell towers
signicantly affects signal strength and reliability.
5G cell towers typically have a range of 1 to 3
miles in low to mid-band radio areas. However,
obstructions such as buildings, walls, and oors
can further degrade signal quality. As the reliance
on remote work and mobile connectivity grows, it’s
imperative to address these challenges, and bring
the RAN closer to the end-user to ensure quality
performance and user satisfaction.
4.03 Accelerated Data Usage
Voice and data demand and consumption have
increased, and with this comes the expectation for
reliability and accessibility of data for everyday
consumer and workforce applications. This puts
growing demands on the cellular network and
drives network congestion.
Ericsson reports that average mobile data
usage per smartphone globally is projected to
increase from 21 GB in 2023 to 56 GB by 2029
1
.
This gure escalates when considering the
expanding demand for non-smartphone data
applications, including robotics, vehicle eets,
machines, equipment, and other physical assets.
This increasing data consumption worsens the
strain on cellular networks, affecting the overall
connectivity experience.
End-users rely on data communications for both
leisure and work-related activities. For leisure,
this includes streaming movies, social media,
video chatting, and online gaming. For work, data
communications support collaboration, virtual
meetings, simulated training, asset tracking,
digital signage, kiosks, digital commerce, and
more. The continued stress to the network with the
growth of data usage will need to be considered
when thinking about indoor cellular coverage.
1 Ericcson Mobility Report (June 2024)
Global mobile
data trafc
consumption per
smartphone is
expected
to reach
56 GB per
month at the
end of 2029.
1

18
Dense Air Industry Insight 2024
4.04 Massive Trafc
As discussed in #4.03, the industry is experiencing
a supply-demand problem, and this becomes
even more cumbersome as we enter high-trafc
or dense areas. In heavily populated urban
areas, as well as events that bring an increase in
pedestrians and visitors in concentrated locations,
the degradation of cellular signals worsens.
On healthcare and college campuses, the high
density of end-users and connected assets creates
a substantial demand for robust network solutions
to improve cellular experiences. Similarly, hotel
guests often face poor communication quality on
the most crowded days due to high trafc.
These frequently visited locations require
advanced solutions to enhance signal strength and
provide redundancy, ensuring improved reliability
and throughput. Network congestion remains
a signicant challenge for businesses, hotels,
hospitals, and campuses, requiring dedicated
efforts to maintain seamless connectivity and
meet user expectations.
4.05 Legacy & Latency
Cellular latency refers to delays or lags in data
transmission, often caused by outdated or
degraded hardware components within the
network infrastructure. Older buildings may also
lack the equipment to properly set up and install
the solutions needed. As equipment ages, it may
struggle to process data efciently, leading to
slower response times and increased latency
for users. This can negatively impact various
activities such as video streaming, online gaming,
or real-time communication, resulting in a less
satisfactory user experience.
Upgrades, and technology refreshes can help
alleviate latency issues and improve overall
network performance. Professionals in-house or
hired will need to perform a complete analysis of
all wired and wireless connectivity installed within
a building, to provide recommendations and
implement solutions that work across all methods
of both voice and data communications.
4.06 Expertise & Skillset Gaps
IT departments may lack the in-house expertise
to modernize their wireless networks. Generally,
legacy IT employees have a strong understanding
of wired communications, traditional networking,
telecommunications, and Wi-Fi, but they lack
complex cellular networking expertise and/
or cannot manage relationships with the large
carriers. Traditionally, IT departments have relied
on third-party vendors, partners, and integrators
to address connectivity challenges. However, the
cellular landscape is changing rapidly. Network
improvements and upgrade cycles are becoming
more frequent, and hardware and equipment
options are evolving at a fast pace.
Keeping up with these evolving solutions, ensuring
seamless 4G to 5G migration, and meeting the
demands of end-users and business performance
can be both costly and time-consuming. Adapting
to these changes requires continuous investment
and effort to maintain optimal connectivity and
performance.
4.07 Secure Connectivity
In today’s digital era, the security of cellular
connectivity is paramount for both personal and
business communications. With the widespread
adoption of 5G technology, which supports
everything from mobile devices to Internet of
Things (IoT) applications, the network architecture
introduces signicant complexities and potential
security vulnerabilities.
Consumers expect robust security measures to
ensure their data remains protected and private,
which is crucial for supporting personal privacy,
business integrity, and national security. The
expansion of connected devices heightens these
security risks, requiring stringent protections
across all network endpoints.
As 5G continues to evolve, maintaining strong
security protocols — through robust encryption,
continuous monitoring, and collaboration among
industry stakeholders — is essential to ensure safe
and reliable connectivity.

19
Dense Air Industry Insight 2024
4.08 Single Carrier
Ensuring that a network supports multiple carriers is paramount to
providing quality cellular connectivity for all tenants and guests,
who likely subscribe to different providers. However, creating a
multi-provider system is challenging due to the technical and
logistical complexities involved.
A single carrier
solution is not a
solution at all.
Each carrier has its specic requirements and frequencies,
which means a solution must be carefully designed to meet
these varied specications without interference.
Additionally, the negotiation process with multiple carriers
can be intricate and time-consuming, as agreements must
be reached that satisfy all parties involved, often requiring
extensive coordination and signicant upfront investment,
as well as pre-existing familiarity and relationships with the
carriers.
Most importantly, the carriers may not prioritize the same
venues: while one building might receive investment from a
carrier with many customers as tenants, other carriers might
choose not to participate in the system.
20
Dense Air Industry Insight 2024
5. Solution Review
Now let’s explore some of the solutions to address the problem of
in-building connectivity. A comparison of three solutions to improve
user access is demonstrated below: Wi-Fi, Distributed Antenna
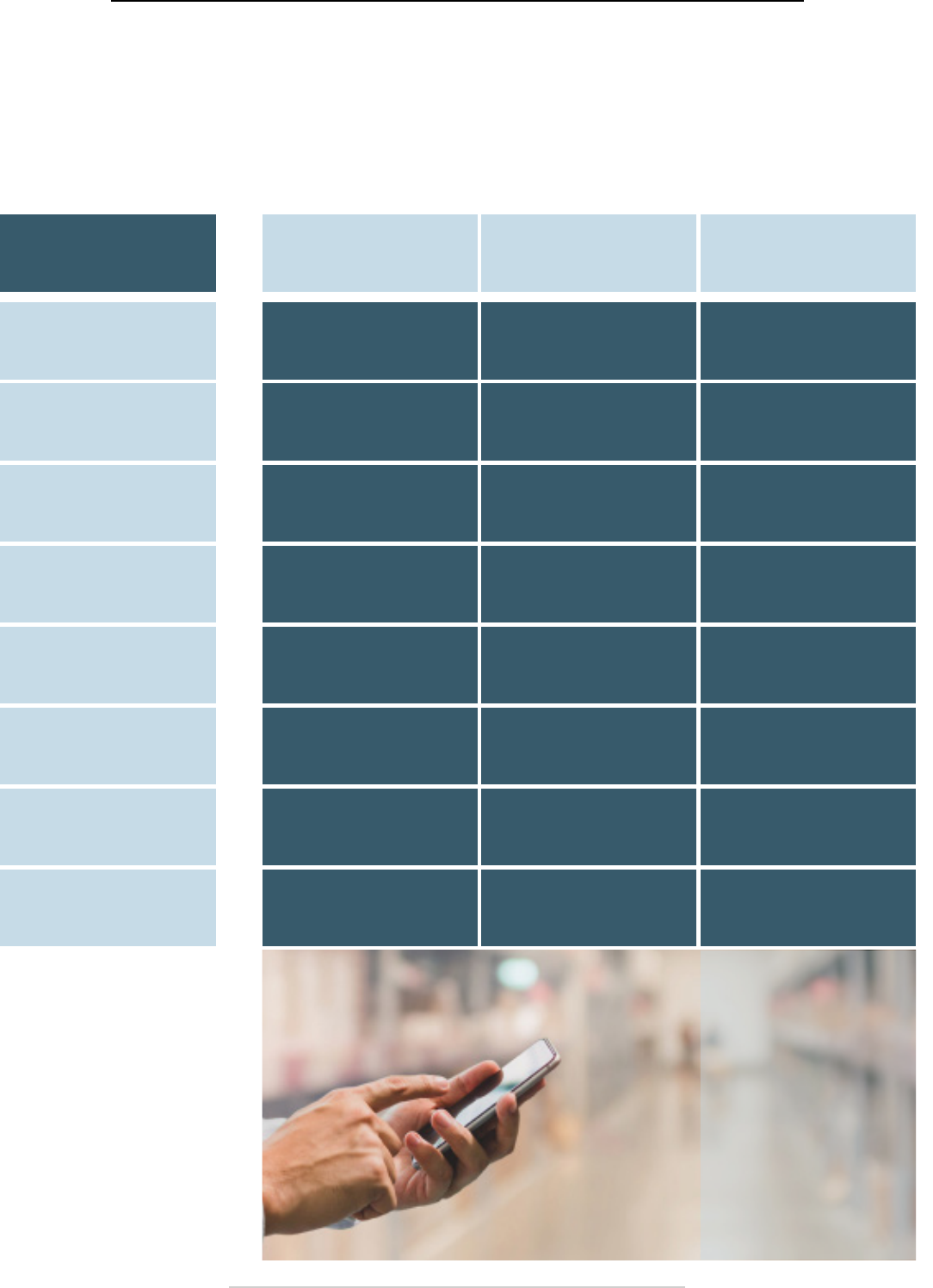
Systems (DAS), and Neutral Host Small Cell (NHSC).
Solution
Comparision
Neutral Host
Small Cell
Wi-Fi DAS
Multi carrier
inclusive
Included as
standard
Passpoint required
to support all
Pay per carrier
onboarding
Carrier
onboarding
Day 1
No
(passpoint required)
9+ months
Uninterupted
calls
Car door to
ofce door
Intermittent Yes
Cost to
build/own
$$
$$ $$$$
Speed to
deploy
6-12 weeks
6-12 weeks 6-18 months
End-to-end
support
Yes
Minimal Yes
Security
Carrier grade
as standard
Minimal, requires
additional requests
Carrier grade
as standard
Scalibility
Yes
Yes No

21
Dense Air Industry Insight 2024
Wi-Fi enables seamless access to the internet and internal networks, fostering
productivity and collaboration among customers and employees. However,
relying on Wi-Fi for wireless connectivity can have its drawbacks. Guests must
have a password for access, making network entry time-consuming and
sometimes challenging. Users expect continuous connectivity as they move
throughout a building – from their car to the building, up the elevator, and into
their ofce. With capacity constraints and coverage limitations, Wi-Fi networks
cannot guarantee a seamless connection, resulting in dropped connections
and user frustration.
5.01 Wi-Fi
Features
Wireless Access: Access to Internet and local networks,
eliminates need for cables
Multiple Device Support: Supports wide range of devices
Scalability: Easily expanded with added access points to
cover larger areas
Ease of Deployment: Easy to install and set up compared to
wired networks
Variety of Standards: Based on speed, range, and capabilities
Flexible Conguration: Congure networks for guests,
business, public
Convenience and Flexibility: Connect from anywhere within
reach
Cost-Effective: Less expensive installation/maintenance
than wired networks
Ease of Use: Minimal setup, making it user-friendly
Scalable: Add access points as you grow or upgrade to newer
Wi-Fi standards.
Compatibility: Compatible with a wide range of devices and
operating systems
Benets

22
Dense Air Industry Insight 2024
Voice Capabilities: Struggles to support calls particularly
when device is mobile
Security Vulnerabilities: Access, data interception, and
cyber-attack risk
Interference: From devices, networks, and obstacles causing
performance issues
Limited Range: Limited range/coverage in multi-oor
buildings & older structures
Network Congestion: High volume of devices or users can
overload the network
Bandwidth Limitations: Lower bandwidth compared to wired
networks
Access Control: Risky environments in public spaces or large
events
Maintenance: Ongoing maintenance and updates for
security and performance
Drawbacks
5.02 Distributed Antenna Systems (DAS)
A DAS improves carrier signals by distributing them to where they are needed,
and then broadcasting them to devices using multiple smaller, less powerful
antennas in various locations. DAS is especially suitable for large-scale, complex
environments where a large area needs to be covered, such as airports and
stadiums. DAS is theoretically carrier-neutral, making it a exible solution
for venues hosting users from different network providers. This technology is
crucial in large or complex structures where conventional wireless networks
might struggle due to interference or distance. By bolstering signal strength and
reducing dead zones, DAS improves productivity, customer satisfaction, and
operational efciency.
Features
Signal Distribution: Strategic placement of antennas to
distribute cellular signals
Scalability: Scale from small to large footprints including
campuses or stadiums.
Multi-Carrier Support: Supports multiple carriers and
frequencies

23
Dense Air Industry Insight 2024
Benets
Drawbacks
Customizable Coverage: Per specic requirements and
usage in the building
High Capacity: Adaptable to high volume of users/devices
simultaneously
Seamless Handoff: Seamless connectivity as users move
through coverage area
Enhanced Coverage: Improve weak signals or dead zones
Improved Signal Quality: Reduce dropped calls and improve
data speeds
Multi-Carrier Support: Users from different mobile networks
supported
Increased Capacity: Enhance high user density for venues
and buildings
Future-Proof: Support upgrades to new frequencies and
technologies (5G)
Customizable: Tailor needs to building, facility, and usage
High Initial Cost: Signicant upfront costs for equipment,
design, and installation
Complex Installation: Greater planning and coordination,
disruption to the environment
Maintenance: Ongoing maintenance for performance
optimization
Long Deployment Time: Due to carrier integration delays
Interference and Capacity Management: Requires greater
skillset and coordination
Carrier Agreements: Multi-carrier agreements require
complex negotiations and each carrier bringing separate
circuits
24
Dense Air Industry Insight 2024
Small cells are low-powered radios that ll in the cellular coverage gaps in
hard-to-reach places, including densely populated areas and in multi-oor
buildings. Small cell technologies can operate in licensed and unlicensed
spectrum that provide a range of 10 meters to several hundred meters. They
ensure comprehensive coverage by mitigating the shorter range and poor
indoor penetration associated with higher frequencies. NHSC does all of this,
while supporting more than one carrier.
5.03 Small Cell and Neutral Host Small Cell (NHSC)
Features
Low-Powered Radio Access Nodes: Enhance cellular
coverage/capacity in localized areas
Neutral Host Capability: Supports multiple carriers at the
same time
Flexible Deployment: Indoor and outdoor application to ll
coverage gaps and enhance network density
High Data Throughput: Low Latency, suitable for data-
intensive applications
Integration with Existing Networks: Works with macrocell
networks for seamless coverage
Scalability: Add more small cells to cover larger areas as you
grow
Enhanced Coverage: Improves indoor environment
connectivity and urban canyons
Cost-Effective: More cost-effective for improving coverage
and capacity in specic areas
Supports Multiple Operators: Supports multiple carriers at the
same time
Increased Capacity: Reduce congestion in high-trafc, dense
areas
Low Latency: Helps real-time data transmission
Flexibility: Adaptable to ofces, hotels, shopping malls, and
urban areas
Reuse existing assets: can use existing building data circuits
(DAS requires carrier provided circuits)
Building Analytics: provides coveted footfall and heatmap
data of cellular users in the building
Benets

25
Dense Air Industry Insight 2024
Complex Coordination: Multiple carrier coordination brings
complexity
Initial Deployment Cost: Upfront costs required, though less
than macrocell
Interference Management: Requires skillful planning and
expertise
Backhaul Requirements: Needs robust backhaul connectivity
to ensure high performance
Limited Coverage Area: Reach limitations compared to
macrocells
Ongoing Maintenance: Requires ongoing maintenance and
monitoring
Drawbacks
6.0 Working with the Right Partner
When a venue owner decides to install an in-building system, there
are several partnership models to consider: in-house, carrier-
deployed, system integrator, and third-party operator (3PO). Each
model has its benets and drawbacks depending on the specic
needs and capabilities of the building owner.
While some building owners with large IT teams may choose to task their in-
house teams with creating the in-building system, most lack the capabilities
to do so and look to partners to build the network and bring the carriers on as
tenants.
Building owners may work with IT integrators who construct the in-building
system but lack the relationships or technical sophistication to bring even a
single carrier onto the network. This leaves the building owners with a stranded
investment and a chronic connectivity problem. Alternatively, owners may turn
to third party operators (3PO) who can build and own the network and work
to bring the carriers on; however, many 3POs overstate their ability to attract
multiple tenants, requiring owners to be skeptical of upfront claims.

26
Dense Air Industry Insight 2024
Selecting the right partner for implementing and installing a seamless cellular
solution is crucial for ensuring optimal performance, cost-efciency, scalability,
and multi-carrier capability.
In-House: Building and managing a system in-house requires signicant
IT expertise and resources. While it offers the highest level of control over
the system, it also involves substantial risks, including the complexities of
carrier coordination and the technical challenges of system management.
This option is usually not feasible for most building owners due to the high
initial investment and ongoing operational requirements.
Direct to Mobile Network Operator (MNO): Going directly to an MNO might
seem like a straightforward approach, but it typically results in a system
that supports only that specic operator’s network. This could signicantly
limit the system’s utility for occupants who subscribe to different carriers,
thereby reducing the system’s overall value and appeal.
System Integrator: System integrators can provide customized solutions
by integrating various subsystems and ensuring they work together
seamlessly. While they are highly skilled in the technical aspects of
DAS installation, their focus is more on the hardware and software
integration rather than ongoing operations or carrier relationships. This
can be a limitation for building owners looking for comprehensive service
management and certainty on attracting multiple carriers.
Third-Party Operator (3PO): A 3PO specializes in managing the entire
lifecycle of an in-building project, from design and installation to operation
and maintenance. The most compelling argument for choosing a 3PO is
their ability to design a DAS with the needs of multiple MNOs in mind. This is
crucial for ensuring wide coverage and compatibility. Furthermore, 3POs are
experienced in negotiating with various MNOs, acting as an intermediary
that can effectively manage relationships and expectations on behalf of
the building owner. This reduces the complexity for the owner and ensures
a DAS that is optimized for performance and protability, with potentially
faster deployment times and minimized operational hassles.
Given these options, partnering with a 3PO often makes the most sense for
building owners. A 3PO not only alleviates the burden of technical and managerial
challenges but also brings expertise in dealing with multiple carriers, ensuring
that the DAS meets the broadest possible needs and maximizes both service
quality and revenue potential. This model provides a balance of technical
prociency, operational management, and carrier negotiation that is difcult to
achieve with other partnership models.
Ultimately, however, a partner is only as good as the technology
deployed. Most 3POs deploy DAS, which requires each carrier to
bring its own separate radio, creating friction and uncertainty of
multi-carrier deployment. When deployed as part of the right
platform, the NHSC alleviates this carrier uncertainty and solves the
cellular connectivity problem quicker.

27
Dense Air Industry Insight 2024
™
TM

28
Dense Air Industry Insight 2024
cellShare™ by Dense Air is a unique solution that offers turnkey
services to identify connectivity gaps, install hardware, implement
software, and offer full-service management of cellular connectivity
improvements.
Dense Air provides the equipment, manages deployment, ensures
security, provides ongoing maintenance, and monitors trafc to
simplify improving cellular connectivity in building.
Primary features of the cellShare™ solution include:
7.0 cellShare™
Enabling multiple carriers at the same time, in the same
location, without waiting months or years after deployment
Cost efcient, minimal footprint, and easily integrated into
the existing buildings.
Rapid installation (weeks) compared to traditional solutions
(months and years)
Security, continuity, and reliability of your cellular connection
Fully managed as a turnkey service
Dense Air incorporates neutral host (or multi-carrier) small cells to solving the
issues of poor connections, dropped calls, and poor cellular experiences with its
cellShare™ solution. The solution can be installed space by space or oor by
oor for multi-oor buildings, which allows for a customized solution that targets
trouble areas and quickly improves end user experiences.
To identify where coverage and capacity gaps exist, cellShare™ uses big data
analytics with a proprietary software tool called denseWare™ that gathers
insights across multiple operators and end-user activity. Dense Air designs
customized solutions and rapidly deploys small cells only where needed, using
existing infrastructure to limit the cost expenditure.
Once cellShare™ is deployed, consistent, reliable 24/7/365 performance
monitoring is enabled, and maintenance and upgrade support are provided
as needed. Through denseWare™, Dense Air provides the software and APIs
(Application Programming Interfaces) needed to fully integrate with existing
systems, provide user and network insights, and present dashboard visibility for
managers or IT teams.

29
Dense Air Industry Insight 2024
Key benets offered via the cellShare™ solution include:
Increased throughput of signal for optimal experiences
Reliable turnkey and white-glove service
Scalable and secure connectivity
Budget-friendly solution with a lower TCO (Total Cost
Ownership), exible opex, and/or capex funding
Less complex and faster installations
Integrates with top carriers simultaneously
Public and private wireless friendly
Network coverage mapping and analytics platform
As businesses digitally transform and automate, cellular remains a
critical foundation for innovation. While cellular is enhancing customer
experiences, it is also being used to augment, improve, or provide
redundancy in enterprise or business networks. Cellular connectivity can
be used to extend or supplement businesses’ primary networks, augment
an existing DAS network, and extend key guest or customer services to
hard-to-reach indoor and outdoor locations.
cellShare™ by Dense Air provides reliable, uninterrupted cellular connectivity
for a fraction of the cost of other options, while improving overall guest
and employee satisfaction, loyalty, and tenant retention — ultimately
maximizing the value of your property.

30
Dense Air Industry Insight 2024
For more information on
cellShare™ please contact
Dense Air at:
www.denseair.net
TM

